This section describes the interface of the SimProject plug-in and the algorithm used.
Contents
With the help of the plug-in SimProject, project plans can be imported from Microsoft Project, parameterized and then simulated and optimized. Figure 1 shows the user interface of the plug-in, with imported project plan.
In the uppermost area of the plug-in window is the menu, in which for example a new project plan can be read in.
Below in the middle area is the configuration view, in which, as in MS Project, the imported project plan is displayed once as a list and once as a Gantt chart.
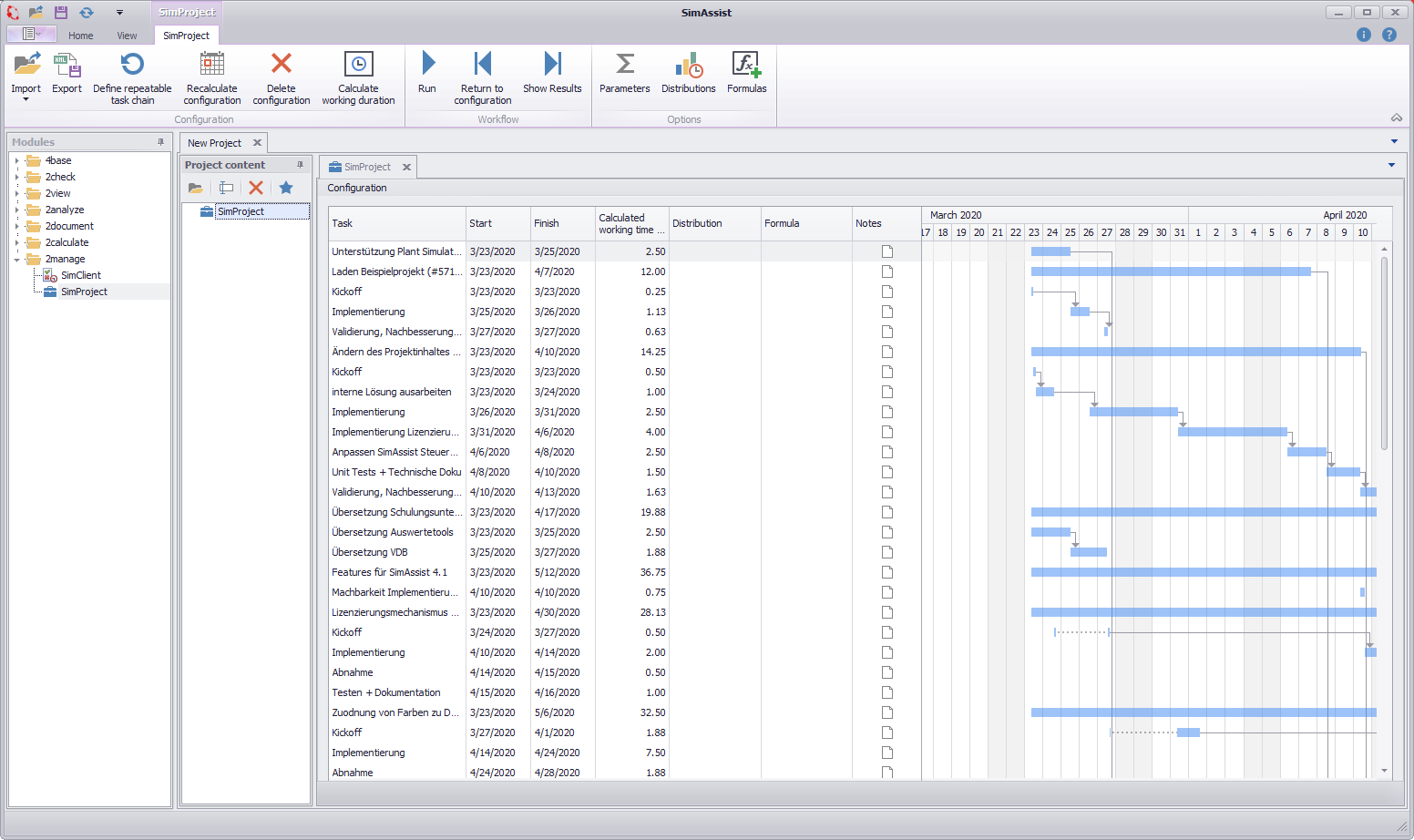
Figure 1 - Overview
|
Information If a new MS Project project plan is read in, an attempt is made to create an assignment between the new and old tasks and to transfer settings (e.g. distributions, formulas) from the old to the new tasks. For this assignment a so-called GUID is used. In addition to the GUID, the "path" of a task is also stored. This path is composed of the name of the task and the names of all parent collective tasks in the imported plan. The path must be unique (otherwise an error message appears when reading in the plan). When reading in the plan, the assignment is first attempted on the basis of the GUID and then on the basis of the path. If you save in MS Project via Save as, MS Project assigns new GUIDs for all tasks. However, by additionally saving the path for each task, this does not pose a problem. However, if new names are assigned to tasks and then the Save as function is used, the settings are lost. |
|
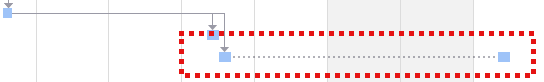
Information Vacation times are taken from MS Project plans. If an existing task is split by a vacation, the split is shown dotted in the graphical view of the project plan:
|
|
Information Collective tasks defined in MS Project are not displayed to better highlight the repeatable chains. |
A genetic algorithm is used to optimize the sequence of tasks.
Initially, depending on the population size parameter (see Options - Editors 1. Parameter Editor), several random sequences are formed and their fitness is evaluated.
If a sequence does not satisfy the predecessor/successor relationships defined in the project plan, it receives a negative fitness.
Otherwise, a project plan with this task sequence is created and simulated. The shorter the average project duration of the simulation runs, the higher the fitness of the sequence is evaluated.
In the genetic algorithm, the "fittest" sequences are combined into new sequences and modified by random "mutations".
The fitness of the newly formed sequences is then also evaluated. At the end of an optimization iteration, the "fittest" sequences are stored and the optimization loop starts again.
The optimization ends if no improvement of the "fittest" sequences was found after a certain number of iterations.
These are then output as results and simulated again to increase statistical confidence.
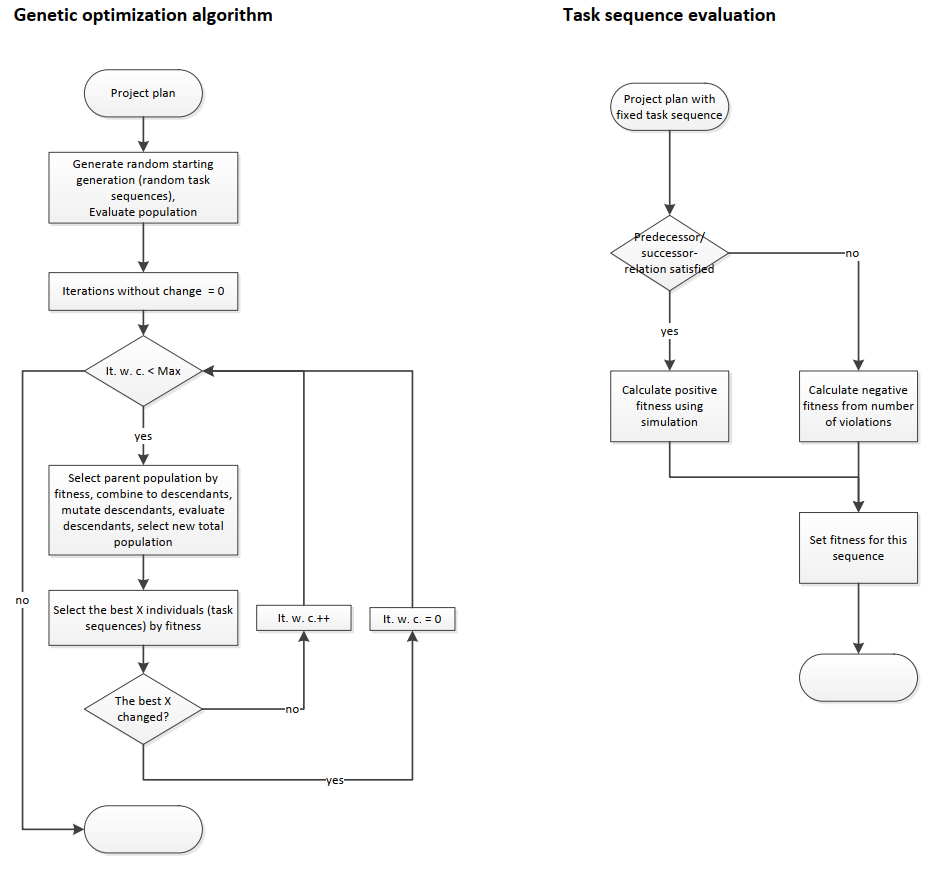
Figure 2 - Algorithm used
© SimPlan AG - Hanau District Court, Commercial Register (Part B) 6845 - info@simplan.de - www.simplan.de/en